DHH-B MAX
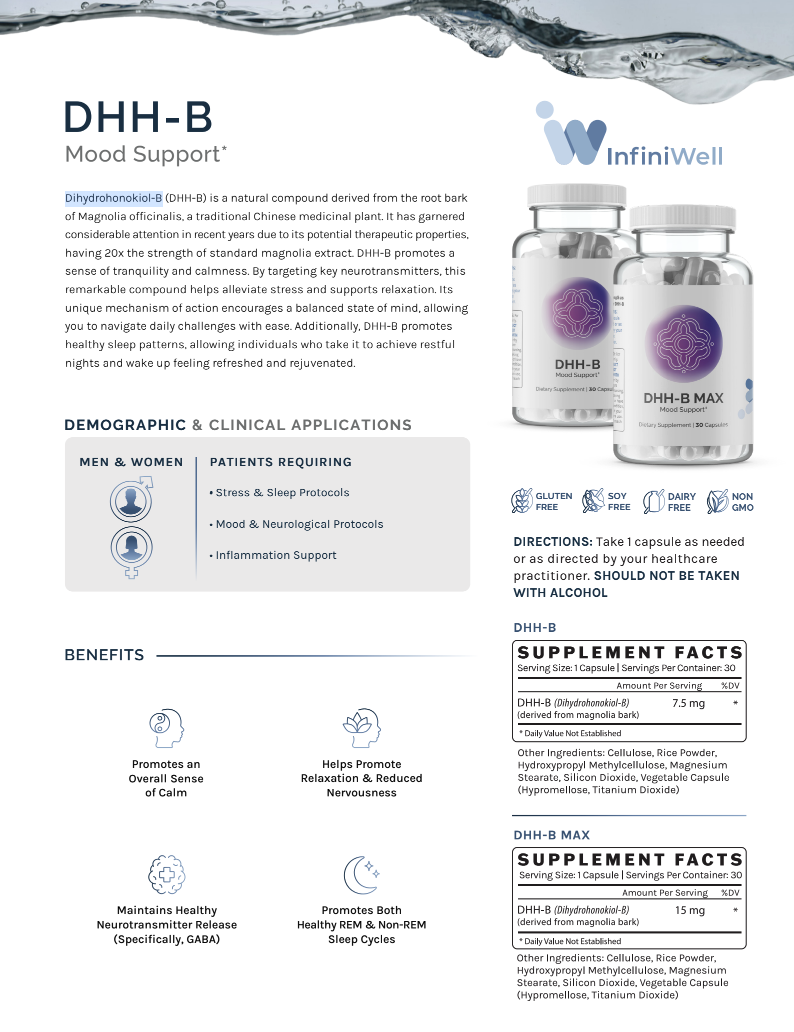
Mood Support*
- Promotes an Overall Sense of Calm
- Helps Promote Relaxation & Reduced Nervousness
- Maintains Healthy Neurotransmitter Release (Specifically, GABA)
- Promotes Both Healthy REM & Non-REM Sleep Cycles
Active Ingredient: DHH-B (Dihydrohonokiol-B)
Other Ingredients: Cellulose, Rice Powder, Hydroxypropyl Methylcellulose, Magnesium Stearate, Silicon Dioxide, Vegetable Capsule (Hypromellose, Titanium Dioxide)
Take 1 capsule as needed or as directed by your healthcare practitioner.
As needed
1 Capsule
SHOULD NOT BE TAKEN WITH ALCOHOL.
-
Benefits
- Promotes an Overall Sense of Calm
- Helps Promote Relaxation & Reduced Nervousness
- Maintains Healthy Neurotransmitter Release (Specifically, GABA)
- Promotes Both Healthy REM & Non-REM Sleep Cycles
-
Ingredients
Active Ingredient: DHH-B (Dihydrohonokiol-B)
Other Ingredients: Cellulose, Rice Powder, Hydroxypropyl Methylcellulose, Magnesium Stearate, Silicon Dioxide, Vegetable Capsule (Hypromellose, Titanium Dioxide)
-
How To Use
HOW
Take 1 capsule as needed or as directed by your healthcare practitioner.
WHEN
As needed
DOSE
1 Capsule
NOTES
SHOULD NOT BE TAKEN WITH ALCOHOL.
DHH-B MAX
Mood Support*
-
OVERVIEW
OVERVIEW
-
IMPACT ON GABA AND OTHER NEUROTRANSMITTERS
DHH-B exerts its biological effects through multiple mechanisms, contributing to its diverse pharmacological activities. One of its primary mechanisms of action is through GABAergic modulation. It acts as a positive allosteric modulator of gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) receptors, enhancing GABAergic neurotransmission.
In addition to its GABAergic effects, DHH-B also influences the release and reuptake of various other neurotransmitters, including dopamine, serotonin, and norepinephrine. By promoting levels of these neurotransmitters, DHH-B exhibits potential support for mood, relaxation, and coganative function. -
ANTIOXIDANT SUPPORT
Another important aspect of DHH-B is its ability to support the production of cytokines such as tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α) and interleukins (IL-1β, IL-6).
Furthermore, DHH-B displays robust antioxidant properties. It is a scavenger of reactive oxygen species (ROS) and upregulates endogenous antioxidant enzymes. These antioxidant effects contribute to its neuroprotective and anti-aging properties. DHH-B’s antioxidant and neuroprotective properties make it a candidate for supporting neurologic physiology and functionality to promote both short term and long term brain health. -
REFERENCES
1. Lin Y, Li Y, Zeng Y, Tian B, Qu X, Yuan Q, Song Y. Pharmacology, Toxicity, Bioavailability, and Formulation of Magnolol: An Update. Front Pharmacol. 2021 Mar 17;12:632767. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2021.632767. PMID: 33815113; PMCID: PMC8010308.
2. Shen JL, Man KM, Huang PH, Chen WC, Chen DC, Cheng YW, Liu PL, Chou MC, Chen YH. Honokiol and magnolol as multifunctional antioxidative molecules for dermatologic disorders. Molecules. 2010 Sep 16;15(9):6452-65. doi: 10.3390/molecules15096452. PMID: 20877235; PMCID: PMC6257695.
3. Hou Y, Aboukhatwa MA, Lei DL, Manaye K, Khan I, Luo Y. Anti-depressant natural flavonols modulate BDNF and beta amyloid in neurons and hippocampus of double TgAD mice. Neuropharmacology. 2010 May;58(6):911-20. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2009.11.002. Epub 2009 Nov 14. PMID: 19917299; PMCID: PMC2838959.
4. Woo SM, Seo SU, Kubatka P, Min KJ, Kwon TK. Honokiol Enhances TRAIL-Mediated Apoptosis through STAMBPL1-Induced Survivin and c-FLIP Degradation. Biomolecules. 2019 Dec 6;9(12):838. doi: 10.3390/biom9120838. PMID: 31817770; PMCID: PMC6995549.
5. Arora S, Singh S, Piazza GA, Contreras CM, Panyam J, Singh AP. Honokiol: a novel natural agent for cancer prevention and therapy. Curr Mol Med. 2012 Dec;12(10):1244-52. doi: 10.2174/156652412803833508. PMID: 22834827; PMCID: PMC3663139.

| Ingredients | Amount Per Serving |
| DHH-B (dihydrohonokiol-B) (derived from magnolia bark) | 15 mg |
Other Ingredients: Cellulose, Rice Powder, Hydroxypropyl Methylcellulose, Magnesium Stearate, Silicon Dioxide, Vegetable Capsule (Hypromellose, Titanium Dioxide)
Professional Information
People Requiring:
-
Stress & Sleep Protocols
-
Mood & Neurological Protocols
-
Inflammation Support
DHH-B Max Antioxidant Supplement: FAQs
Have more questions? We have answers
InfiniCare—your personal concierge for longevity. Our team of experts, including our on-staff physician, are standing by to ensure world-class service.
Our team is located in Dallas, TX, USA
-
What is DHH-B Max?
DHH-B Max by InfiniWell is a dietary supplement formulated with dihydrohonokiol-B (DHH-B), a naturally derived compound sourced from magnolia bark. It is designed to support relaxation, balanced mood, and healthy neurotransmitter activity.DHH-B has been studied for its calming properties and its support of natural relaxation pathways. Related research on magnolia-derived compounds has explored how these compounds interact with neurotransmitter systems involved in relaxation. -
What does DHH-B Max support?
DHH-B Max is formulated to support overall mental and emotional well-being, especially during periods of everyday stress. When used thoughtfully, potential DHH-B benefits may include:- Support for a calm, relaxed mood
- Help maintaining emotional balance during everyday stress
- Support for healthy neurotransmitter activity
- Support for restful, consistent sleep
- Antioxidant support for overall brain wellness
-
How does DHH-B support relaxation and mood?
DHH-B is associated with supporting healthy GABA signaling. GABA is a naturally occurring neurotransmitter involved in calming neural activity and promoting relaxation.By supporting normal GABA activity, DHH-B Max is designed to help the body maintain a relaxed, balanced state, especially during times of mental or emotional demand. -
Does DHH-B Max cause drowsiness?
DHH-B Max is non-sedating. It is formulated to support relaxation without causing grogginess, making it suitable for daytime use or evening routines, depending on individual needs. -
Can DHH-B Max support sleep?
Yes. DHH-B Max is often used to support sleep quality by encouraging relaxation and helping the body wind down naturally. Rather than forcing sleep, it supports the conditions that allow for more consistent, restful sleep. -
Is DHH-B Max habit-forming?
No. DHH-B Max is not a sedative and is not associated with dependency. It supports the body’s natural relaxation pathways rather than overriding normal brain activity. -
Is DHH-B Max an antioxidant supplement?
DHH-B exhibits antioxidant activity, which may help the body manage oxidative stress that can arise from everyday physical and mental demands.Antioxidants support general wellness by helping neutralize reactive molecules produced during normal metabolism, stress, or environmental exposure. -
How should I take DHH-B Max?
Take 1 capsule as needed, or as directed by a qualified healthcare professional.DHH-B Max is commonly taken:
- In the evening as part of a nighttime routine
- During the day to support calm during stressful moments
-
How quickly does DHH-B Max work?
Many users notice a sense of calm within 30–60 minutes. With continued use, DHH-B Max may support longer-term benefits related to mood balance and sleep quality. Individual experiences may vary. -
Who is DHH-B Max for?
DHH-B Max is designed for healthy adults looking to support relaxation and mental balance, including:- Individuals with busy or demanding schedules
- Adults seeking non-sedating mood support
- Those looking to support restful sleep as part of a wellness routine
-
What makes InfiniWell DHH-B Max supplement different?
InfiniWell DHH-B Max is intentionally formulated with clarity and quality in mind:- Single active ingredient: No proprietary blends or hidden components
- Non-sedating formula: Supports calm without slowing you down
- Stimulant-free: No caffeine or excitatory ingredients
- Third-party tested: Produced in a GMP-certified facility
- Thoughtfully formulated: Designed to support mood, sleep, and overall well-being
-
Can I take DHH-B Max with other supplements?
DHH-B Max can generally be combined with other dietary supplements. Many people pair it with supplements that support sleep, cognitive wellness, or overall nutrition.If you are combining multiple supplements or taking prescription medications, consult a qualified healthcare professional for personalized guidance. -
How can I support my body’s natural antioxidant defenses?
A diet rich in fruits and vegetables is one of the most effective ways to support antioxidant intake. Foods such as berries, leafy greens, citrus fruits, carrots, and tomatoes provide naturally occurring plant compounds that support cellular wellness.Remember, supplement use should complement, not replace, a balanced diet. -
Is there anything to keep in mind when using antioxidant supplements?
Antioxidants support general wellness, but more is not always better. Individual needs vary based on lifestyle, diet, and overall health.Rather than focusing solely on supplements, aim for a consistent intake of antioxidant-rich foods and consult a qualified healthcare professional before adding new supplements to your routine. -
Disclaimer
This content is for general informational purposes only and is not medical advice. Always talk to a qualified healthcare professional before starting any new supplement or making changes to your wellness routine.