DIM
Hormone Support & Detoxification*
- Supports Healthy Estrogen Metabolism
- Promotes Leaner Body Composition
- Aids Liver Detoxification
- Supports Antioxidant Capacity
Active Ingredients: DIM (Diindolylmethane)
Other Ingredients: Microcrystalline Cellulose, Magnesium Stearate, Silicon Dioxide, Vegetable Capsule (Hypromellose, Titanium Dioxide)
Take 2 capsules daily with water or as directed by your healthcare practitioner.
Daily
2 Capsules
-
Benefits
- Supports Healthy Estrogen Metabolism
- Promotes Leaner Body Composition
- Aids Liver Detoxification
- Supports Antioxidant Capacity
-
Ingredients
Active Ingredients: DIM (Diindolylmethane)
Other Ingredients: Microcrystalline Cellulose, Magnesium Stearate, Silicon Dioxide, Vegetable Capsule (Hypromellose, Titanium Dioxide)
-
How To Use
HOW
Take 2 capsules daily with water or as directed by your healthcare practitioner.
WHEN
Daily
DOSE
2 Capsules
Hormone Support & Detoxification*
-
OVERVIEW
In the realm of natural compounds, one has steadily risen to prominence for its potential to enhance overall health and maintain equilibrium in various bodily systems. Diindolylmethane (DIM) is a bioactive substance sourced from cruciferous vegetables such as broccoli, cabbage, and Brussels sprouts. Scientific research has illuminated DIM's remarkable contributions to well-being, with its primary areas of applications focusing function and cellular health.
-
KEY FUNCTIONS
Balancing Hormones
DIM's first major feat lies in hormonal equilibrium. It engages in a crucial role by aiding in the metabolism of estrogen, a hormone that wields significant influence over health. Through a series of metabolic transformations, DIM encourages the conversion of potent forms of estrogen, like estradiol (E2), into less active metabolites such as 2-hydroxyestrone (2-OHE1). This process holds the potential to reduce the risk of health concerns related to estrogen dominance.1
Supporting Detoxification
The body's detoxification pathways form the frontline of defense against harmful toxins and carcinogens. DIM steps into this arena by fortifying phase II detoxification pathways. It promotes the expression and activity of critical detoxifying enzymes, including cytochrome P450, glutathione S-transferases, and quinone reductase. In doing so, it facilitates the elimination of harmful compounds, enhancing the body's detoxification capabilities.2,3
Nurturing the Immune System
DIM's reach extends to the immune system, a vital guardian of health. It modulates immune responses by influencing the production and activity of immune cells, including T lymphocytes and natural killer (NK) cells. The result is a more robust and balanced immune system, ready to fend off threats and maintain well-being. 4,5
Guarding Cellular Health
Amid the bustling landscape of our bodies, cellular health stands paramount. DIM dons the cape of a potent antioxidant, swooping in to shield cells from oxidative stress and the perils of free radical damage. This guardian of cells bolsters the body's innate defenses against oxidative harm, combating the aging process and potentially lowering the risk of oxidative stress-related diseases.6,7
-
REFERENCES
1. Bradlow, H. L., et al. (1991). Long-term responses of women to indole-3-carbinol or a high fiber diet. Cancer Epidemiology, Biomarkers & Prevention, 1(5), 345-351.
2. Reed, G. A., et al. (2005). A phase I study of indole-3-carbinol in women: tolerability and effects. Cancer Epidemiology, Biomarkers & Prevention, 14(8), 1953-1960.
3. Lord, R. S., et al. (1997). Urinary metabolites of indole-3-carbinol in humans and rats. Chemical Research in Toxicology, 10(12), 1228-1233.
4. Ge, X., et al. (2013). Indole-3-carbinol inhibits LPS-induced inflammatory response by blocking TRIF-dependent signaling pathway in macrophages. Food and Chemical Toxicology, 53, 56-64.
5. Kim, Y. H., et al. (2019). Diindolylmethane suppresses the growth of 5-fluorouracil-resistant colorectal cancer cells through the activation of the p38 MAPK pathway. Oncology Letters, 18(3), 2577-2586.
6. Rahman, K. M., et al. (2008). Dietary indoles suppress delayed-type hypersensitivity by inducing a switch from proinflammatory Th17 cells to anti-inflammatory regulatory T cells through regulation of microRNA. Journal of Immunology, 180(1), 659-669.
7. Al-Malki, A. L., & El Rabey, H. A. (2015). The antidiabetic effect of low doses of Moringa oleifera Lam. seeds on streptozotocin induced diabetes and diabetic nephropathy in male rats. BioMed Research International, 2015, 381040.

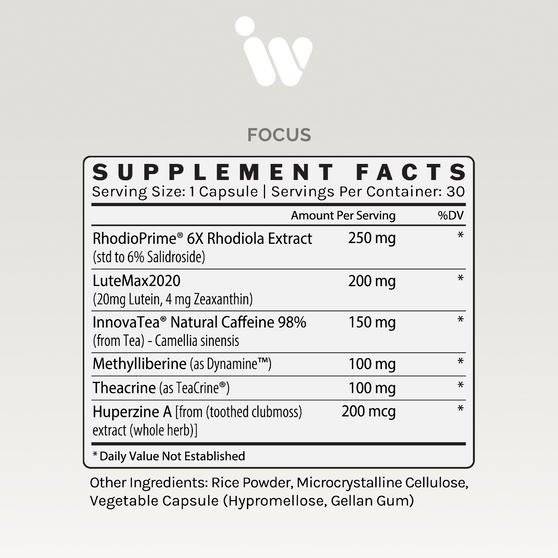
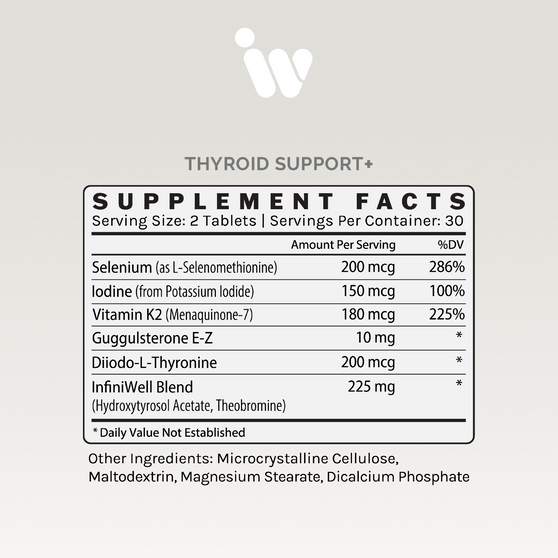
| Ingredients | Amount Per Serving |
| DIM (as Diindolylmethane) | 150 mg |
Other Ingredients: Microcrystalline Cellulose, Magnesium Searate, Silicon Dioxide, Vegetable Capsule (Hypromellose, Titanium Dioxide)
Professional Information
People Requiring:
-
Hormonal Balance Protocols
-
Estrogen Dominance Support
-
Phase II Detoxification Support
-
Immune System Maintenance